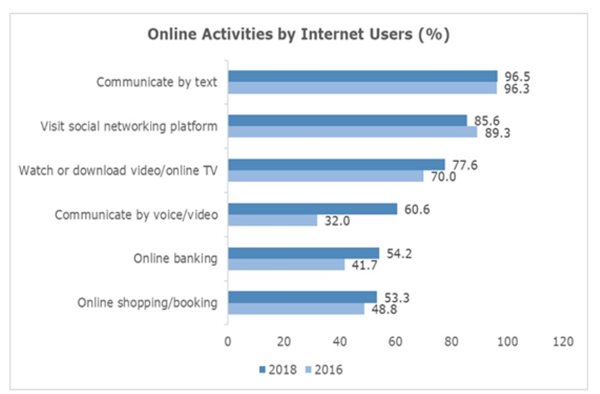
In the same vein as the 1979 song “Video killed the radio star”, in 2018, video and voice calls via social messaging apps are set to take over from traditional voice calls with Internet users in Malaysia increasing their online calls by almost 30% in 2018, compared to 2016. With data becoming increasingly more affordable, this trend is set to become the norm, according to the Internet Users Survey 2018 (IUS 2018) released by the Malaysian Communications and Multimedia Commission (MCMC) today.
A total of 87.4% of Malaysia’s population now use the Internet compared to 76.9% in 2016. Currently, the world average is 51.2% as reported by the International Telecommunications Union (ITU) in its Measuring the Information Society Report 2018.
Two years ago, Malaysia was reported to have had the highest number of Facebook accounts based on population numbers. In 2018, however, the use of social networking services declined by almost 4% compared to 2016 figures (89.3% in 2016, 85.6% in 2018). However, communication via text messages using social messaging applications remains the most popular online activity among Internet users in Malaysia (96.3% in 2016, 96.5% in 2018).
In terms of online content consumption, more viewers are moving from traditional channels to online offerings (70% in 2016, to 77.6% in 2018).
In November 2018, Speedtest Global Index by Ookla reported that fixed broadband download speeds in Malaysia increased by almost threefold to 58Mbps as compared to 23Mbps in January 2018. This development will allow Malaysians, particularly businesses, to maximise their potential income derived from online activities.
Correspondingly, digital transactions are on the uptrend with online banking and shopping increasing in numbers in 2018, compared to 2016. The rising number of Internet users and greater trust in online banking are catalysts in developing a wider digital ecosystem including e-commerce, fintech and various other digital services which contribute to the overall growth of Malaysia’s digital economy.
These user trends are indications of the results of concerted measures put in place such as wider access to 3G and 4G/LTE, improved network quality and increased competition in the mobile broadband market. In addition, measures were introduced to reduce prices and increase the speed of fixed broadband.
The IUS 2018 also found that nine out of ten children in the 5 – 17 age bracket used the Internet making them vulnerable to various online risks such as inappropriate content, cyberbullying, communicating with strangers and online scams. In managing online risks to children, most parents (75.5%) prefer to set their own rules and limits of Internet usage for their children, including being present when their children were online, rather than use available parental control tools (12.2%).
Similar to the finding from the IUS 2016, the IUS 2018 found that most users prefer to access the Internet from home. The IUS 2018 revealed that for both urban and rural users, nine out of ten (88.6%) access the Internet at “home” largely because of being able to work from home, the home being a conducive learning environment for students and the Internet being a primary source of home entertainment. “On-the-go” ranked second (68.1%) followed by the “work place” (56.4%). Accordingly, fewer Internet users accessed free Wi-Fi or visited commercial and community Internet access facilities.
The smartphone remains the top device for accessing the Internet, coming in at 93.1%. The increasing computing power of this device which continues to enable the growth of new applications and functionalities, has led to the decline in accessing the Internet via desktop and feature phones. Meanwhile, home devices such as Smart TVs, TV streaming boxes and game consoles are gaining traction among Internet users, in line with the growth of streaming services.
Faster speeds, cheaper mobile plans and devices as well as bigger data allowances have contributed to the rise in streaming, communication by voice/video, downloading online music and playing online games. For instance, 77.6% of users spent time streaming/downloading online videos as compared to 70.0% in 2016, while 60.6% communicated by voice/video as compared to 32.0% in 2016.
Figure 1: Online activities by Internet users based on IUS 2016 and 2018
“Gathering empirical evidence on changing and emerging consumer trends and analysing it accurately will equip MCMC better to initiate regulatory and developmental measures to support national policy objectives,” said Al-Ishsal Ishak, Chairman of the MCMC.
“A significant finding is that users are engaging in activities requiring high bandwidth capacity and this trend is expected to continue. The National Fiberisation and Connectivity Plan (NFCP) which is being finalized by the Ministry of Communications and Multimedia in collaboration with MCMC and its stakeholders is expected to balance regional growth by creating more opportunities enabled by broadband services. With improved coverage, quality and affordability of broadband, more Malaysians will be able to participate in the digital economy,” he added.
The annual survey, which was carried out between April 26 to August 10, 2018 through telephone interviews, reached a sample of 4,160 Internet users nationwide. Respondents were selected at random.
For more information on the IUS 2018, please visit:
https://www.skmm.gov.my/resources/statistics
[Download PDF]– MCMC Press Release